Networks
Networks are FiFos abstraction for IP assignment. It works pretty much like a DHCP server with handing out IPs to newly created VMs. Networks consist of an IPRange, its networking attributes, and optional DNS servers. It is also possible to set network related scripts.
Networks also have a network tag which allows directing them towards different hosts.
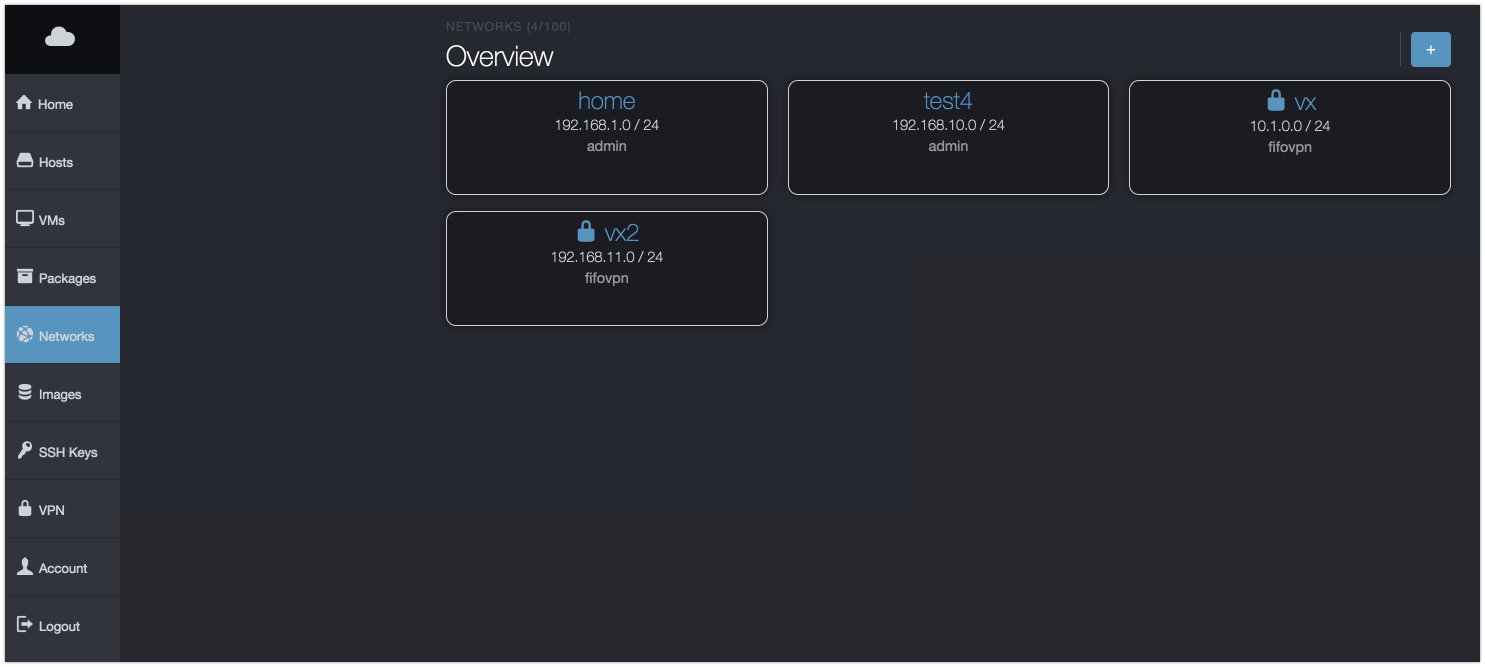
Overivew
The overview shows a list of all networks you have currently available. VPN enabled networks are shown with a lock symbol next to them.
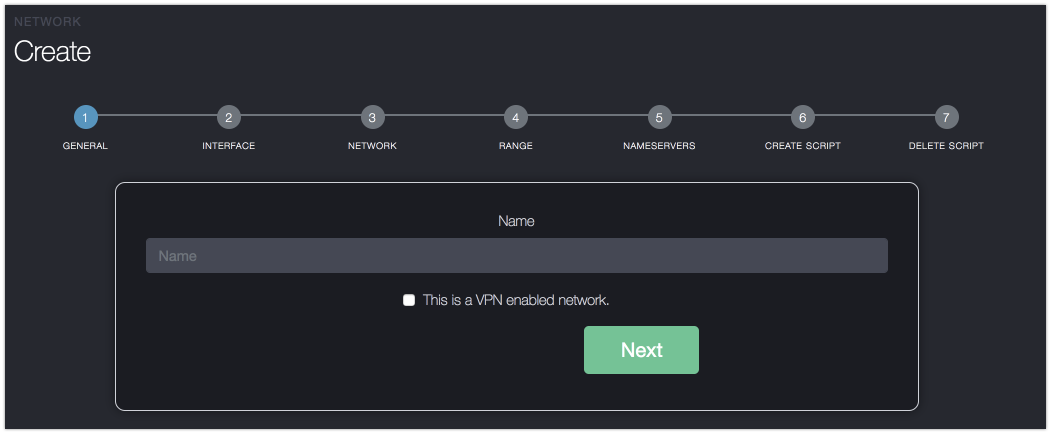
Adding
For adding a network a wizard will take you through the configuration. The following attributes need to be configured.
Note that when creating a VPN enabled network VLAN and Nic Tag can not be changed.
- NIC tag - The nic tag of the interface this network runs on.
- subnet - the subnet for the network
- netmask - the netmask for interfaces created from this network (it does not have to match the subnet!)
- gateway - the gateway for interfaces created from this network
- first - the first IP that is handed out as part of this network
- last - the last IP that is handed out as part of this network
In additional the following optional attributes can be set.
- VLAN - the VLAN ID for the network to use
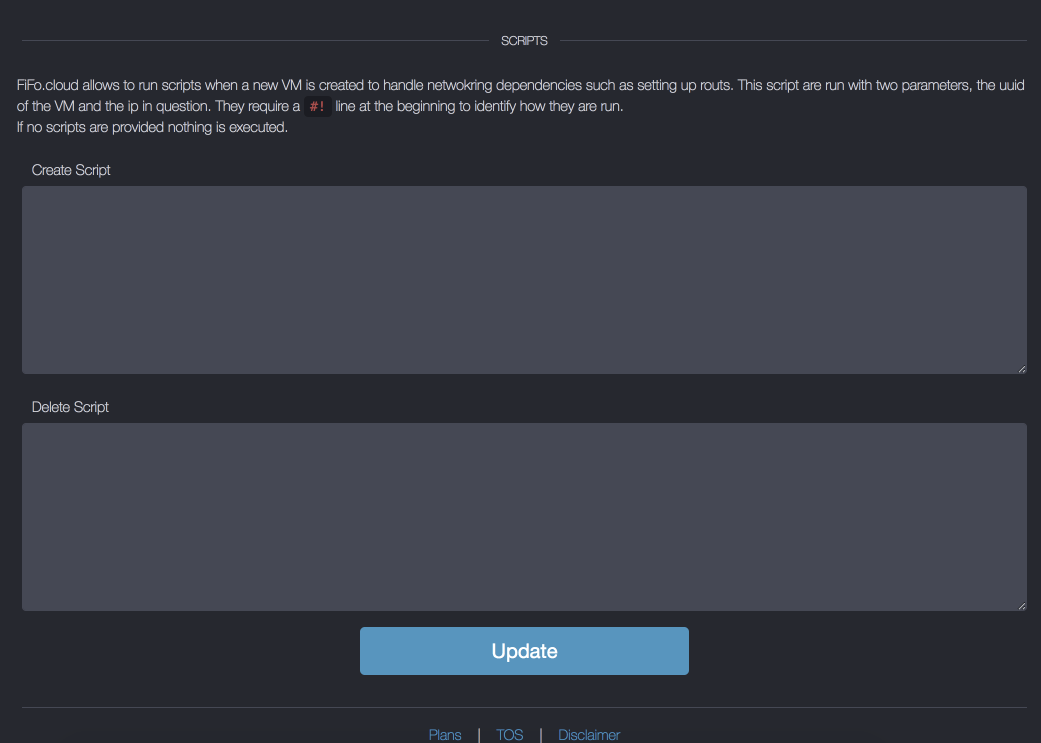
- create script - a script to be executed when a new VM with this network is created, the first argument is the UUID of the VM the second its IP
- destroy script - a script to be executed when a VM with this network is destroyed, the first argument is the UUID of the VM the second its IP
- primary nameserver - the primary DNS server for the VM
- secondary nameserver - the secondary DNS server for the VM
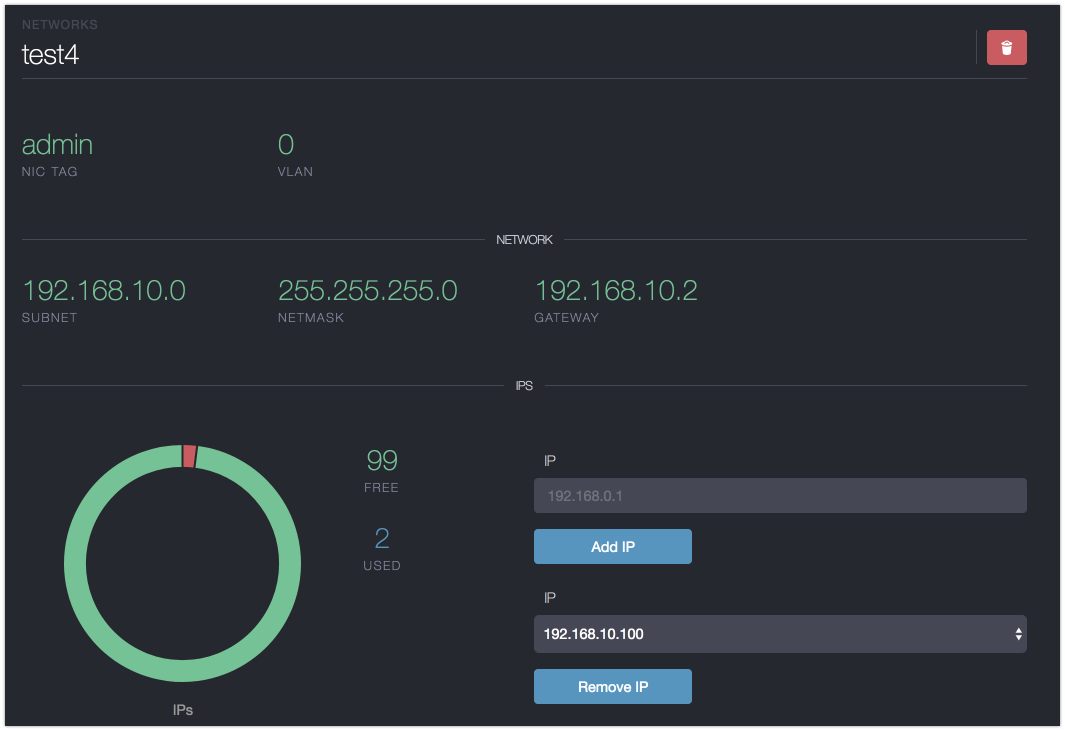
Details
The detail page allows you to view the network details and update scripts; it also gives you an overview of how many IPs of the network are used so far. Here it is also possible to add and remove IPs from the network, this can be handy for netwokrs representing public IP ranges from hosting providers.
Scripts
Networks can have scripts that are run whenever a VM with an interface on this network is attached. This allows for using additional network resources at some cloud providers by doing the required API calls or configuring other network equipment to integrate the VM into your environment.